The Ultimate Guide to the Best Reflow Oven
Table of Contents
- Einführung
- Content
- Step-by-Step Process on How to Use a Reflow Oven
- Common Mistakes and Solutions
- Expert Tips and Best Practices
- FAQs about Reflow Ovens
- Additional Resources and Tools
- Conclusion
Einführung
In the world of electronics manufacturing, particularly in PCB assembly, the reflow oven plays a pivotal role. This guide will provide you with a deep understanding of what reflow ovens are, their significance, and how to make an informed decision when choosing the best one for your needs.
Content
A reflow oven is a vital instrument in the realm of electronics manufacturing, playing a crucial role in bonding surface mount devices (SMDs) onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). This process is essential for creating the robust electrical connections necessary for the reliable functioning of electronic devices. At the core of its operation, a reflow oven utilizes heat to melt solder paste previously applied to the PCB. When the solder melts, it reflows and solidifies upon cooling, forming durable and conductive joints that hold components firmly in place and ensure electrical continuity. For a comprehensive understanding of reflow ovens and their use in electronics manufacturing, you can explore our Guide to Reflow Soldering and Reflow Ovens.
The intricacies of reflow ovens are underscored by the variety of types available, each designed to suit specific applications and preferences within the industry. The three primary types of reflow ovens are convection, vapor phase, and infrared ovens. Each type has its distinct characteristics and operational methodologies, making them suitable for different manufacturing environments and product requirements.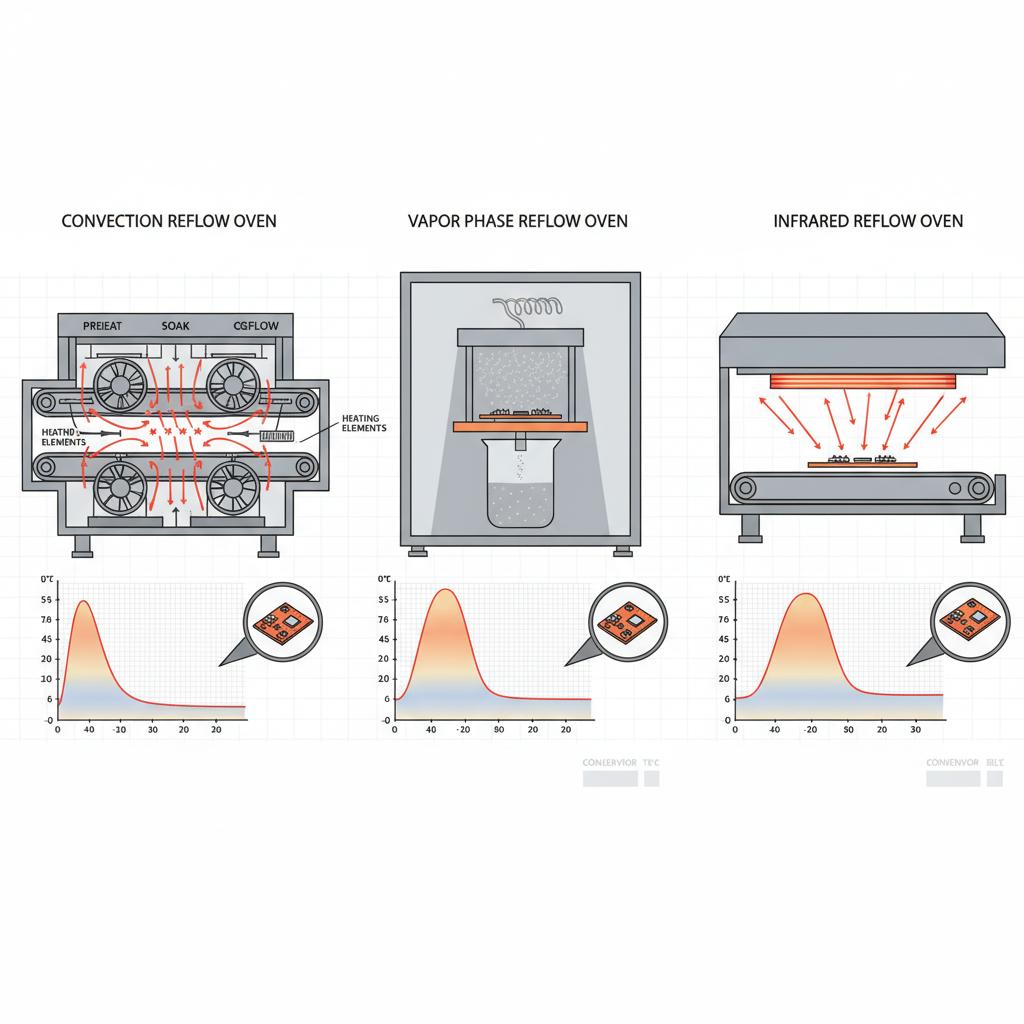
Convection Reflow Ovens
Convection reflow ovens are the most prevalent model used in the industry due to their efficiency and even heat distribution. They operate by utilizing heated air to transfer thermal energy to the PCB and components. Within these ovens, fans circulate hot air throughout a chamber, achieving uniform temperature distribution, which is crucial for the consistent melting of solder across all areas of the PCB. This feature makes convection ovens ideal for mass production settings where reliability and repeatability are paramount.
Vapor Phase Reflow Ovens
Vapor phase ovens present a unique approach to reflow soldering. They use a process that involves a liquid that boils at a pre-set temperature. The boards are passed through this vapor, whose temperature accurately matches the desired soldering temperature. This method ensures that overheating does not occur, as the maximum temperature the board can reach is that of the vapor itself. Vapor phase reflow is particularly beneficial for soldering assemblies with complex, densely packed components, as it minimizes thermal stress and prevents soldering defects that might arise from uneven heating.
Infrared Reflow Ovens
Infrared reflow ovens leverage radiant heat produced by infrared lamps to raise the temperature of the board and solder paste. The efficiency of this type is linked to the absorption of infrared radiation by the components and PCB. One of the challenges with infrared ovens is the potential for non-uniform heating, especially with components that have varying thermal masses. However, these ovens can be effective in scenarios where selective heating is necessary or when dealing with boards that might be sensitive to high temperatures over prolonged durations.
Choosing the Right Reflow Oven
Selecting the right type of reflow oven for a specific application is critical and depends on various factors, including the nature of the components used, the complexity of the assemblies, production volume, and budget constraints. Manufacturers must weigh the precision and control offered by each oven type against their specific requirements.
Overall, understanding the diversity and capabilities of reflow ovens is fundamental for those in the electronics manufacturing sector. Whether you are a novice or a seasoned professional, knowledge of how reflow ovens function and the unique benefits each type offers can significantly impact the quality and efficiency of the production process. With the advancement of technology and the increasing complexity of electronic assemblies, selecting the appropriate reflow oven has become more crucial than ever in ensuring manufacturing success.
Key Benefits of a Reflow Oven
A reflow oven is an essential piece of equipment in the modern electronics manufacturing industry. Here, we’ll explore why this technology is critical for ensuring the highest quality PCB assembly. With insights referencing data and guides from chuxin-smt.com, we provide a detailed look at the key advantages of utilizing a reflow oven.
Enhanced Quality, Cost Efficiency, Increased Efficiency, Versatility [View More]
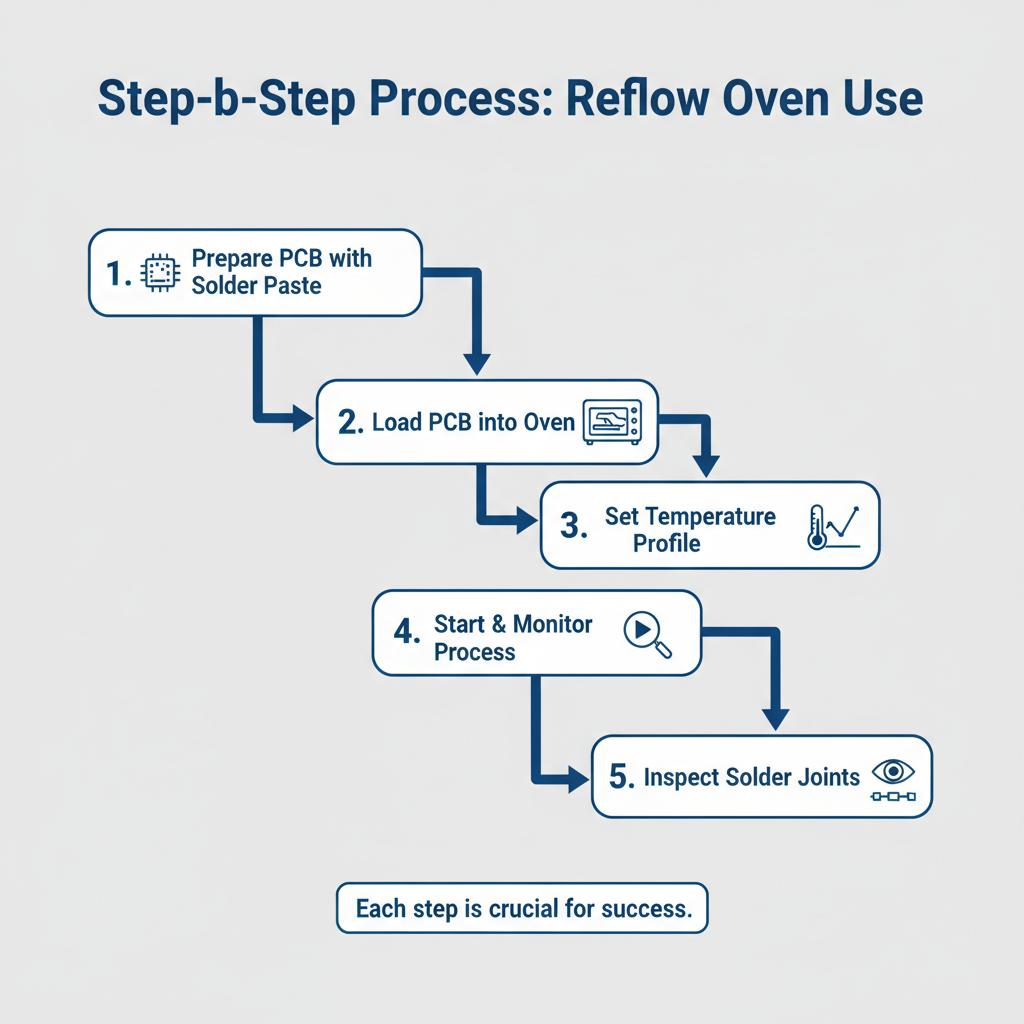
Step-by-Step Process on How to Use a Reflow Oven
1. Prepare the PCB with Solder Paste
The first step in the reflow process involves applying solder paste to the PCB. This is typically done using a stencil to ensure precise application of the paste onto the pads where components will be placed. The paste consists of a mixture of powdered solder and flux, which helps in adhesion and reduces oxidation during the soldering process. Ensuring that the solder paste is evenly and accurately applied is crucial as it directly affects the final solder joint quality. If you’re looking to optimize this stage, check out our Guide to Reflow Soldering and Reflow Ovens for more detailed strategies.
Common Mistakes and Solutions
Improper Temperature Settings, Poor Solder Paste Application, Inadequate Equipment Maintenance [View More]
Expert Tips and Best Practices
Follow Manufacturer’s Specifications, Regular Calibration and Maintenance, Record Temperature Profiles [View More]
FAQs about Reflow Ovens
Q1: What Types of Reflow Ovens are Available?
Additional Resources and Tools
- Recommended Reading on PCB Assembly
- Online Courses for Mastering Reflow Oven Techniques
- Links to Suppliers and Software Tools for Managing PCB Manufacturing Processes
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing the best reflow oven is not just a choice—it’s a strategic decision that can profoundly influence the efficiency and quality of your electronics manufacturing process. Whether you’re a novice stepping foot into the field of electronics or a seasoned professional refining your production capabilities, understanding the intricacies of reflow ovens is vital for optimizing your operations.
Reflow ovens are integral to the PCB assembly process, ensuring that solder joints are formed correctly and reliably. They work by applying controlled heat to solder paste on circuit boards, ultimately producing secure and precise connections between electronic components and the boards themselves. This not only boosts the durability of the final product but also minimizes the risk of defects and failures, leading to higher customer satisfaction and reduced warranty claims.