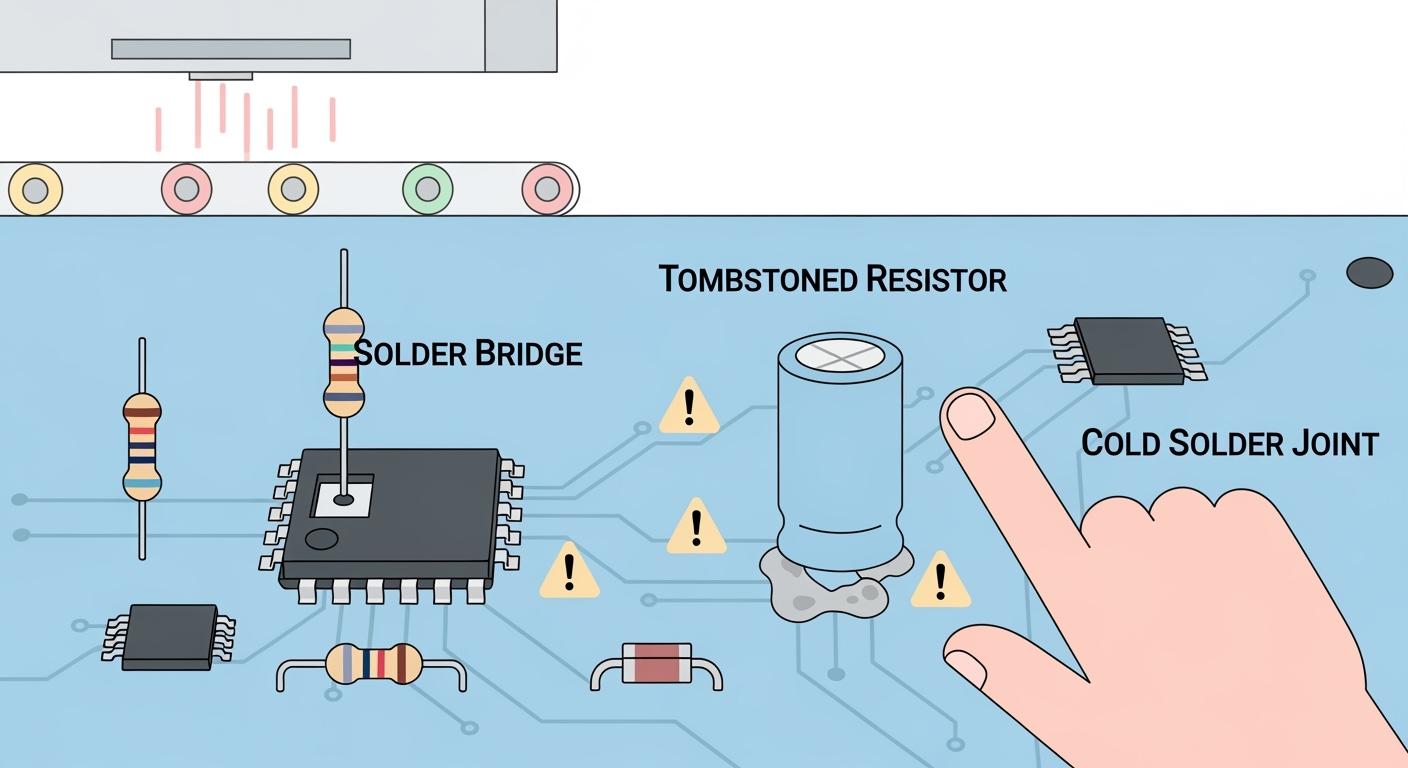
You face many problems in reflow soldering during pcb assembly. High defect rates in reflow can make weak solder joints, cold solder connections, and solder bridging. These solder problems often cause bad electrical connections and lower product quality. You may have to spend more money on fixing things when solder issues happen. To stop these solder defects, you need to use best practices for pcb and component handling. With the right steps, you can have fewer soldering problems and get better results.
Weak solder joints and bridging make products less reliable.
More defects mean you spend more to fix things and get fewer good products.
Principales conclusiones
Make sure to use the right amount of solder paste. This helps stop weak joints and solder bridging. Always check the amount before you start.
Keep your workspace clean to stop contamination. Clean PCBs and parts make solder joints stronger.
Set the reflow temperature profiles correctly for better results. Good heat control means fewer defects.
Use good pad design to stop problems like tombstoning and bridging. Follow IPC standards for the best results.
Check and take care of your equipment often. This helps your equipment work well and lowers soldering defects.
Solder Bridging in Reflow Soldering
What Is Solder Bridging?
Solder bridging happens when solder connects pads that should not touch. You might see a small piece of solder joining two places. This is a common problem in reflow soldering. Solder bridging can make electrical shorts. These shorts can cause your product to stop working.
Causes of Solder Bridging
Many things can cause solder bridging:
Too much solder on pads can make bridges.
Wrong temperature during reflow makes solder move to the wrong spots.
Pads that are too close together make bridging more likely.
If parts are not lined up, leads can touch other pads.
Dirty or damaged pads stop solder from sticking well.
If you do not fix these problems, you will get more solder defects.
Impact on Solder Defects
Solder bridging causes big problems in finished boards. Solder bridges make electrical shorts between pads. These shorts mess up how current flows. Your circuits may not work right. Even one solder bridge can cause trouble in important products. You need to stop these defects to keep your products working well.
Solutions to Prevent Bridging
You can do many things to stop solder bridging:
Control reflow profiles to keep the right temperature.
Use solder masks to block solder from going to wrong places.
Make sure pads are spaced apart in your PCB design.
Put on the right amount of solder paste.

SADOMASOQUISMO’s Nitrogen reflow oven helps you control temperature and keep things steady. This oven helps you get fewer solder defects by making the process even. For quick fixes, check for too much solder, look at your reflow settings, and make sure parts are lined up. Clean pads before soldering to stop dirt problems. If you follow these steps, you can lower solder bridging and make your assembly better.
Tombstoning and Component Shift
What Is Tombstoning?
A tombstone defect happens when one end of a small chip lifts up. The part stands straight, like a tombstone. This happens because solder melts unevenly on each side. One side pulls harder, so the other side lifts. Tombstoning is common in reflow soldering. It can stop your circuit from working.
Causes of Component Shift
Component shift means parts move from their correct spot. You should know what causes these problems to stop defects:
Wrong reflow oven settings
Solder paste problems, like too much or too little
Mistakes when placing parts
If you do not fix these issues, you will get more solder defects. You will also have fewer good boards.
Soldering Impact and Defects
Tombstoning and component shift can hurt your product:
Reworked joints may not last long
Parts can get damaged from too much heat
Production slows down and quality may drop
You want to stop these problems to keep your boards strong and costs low.
Solutions for Tombstoning
You can do many things to lower tombstoning and component shift:
Use the right stencil and solder paste for even wetting
Place parts carefully to avoid mistakes
Make pad sizes match part sizes for better hold
Check and improve your reflow process often
S&M’s reflow oven gives steady rail support and good temperature control. These features help keep parts in place and heat even. If you use best practices and good equipment, you can get fewer solder defects and better results.
Poor Wetting and Cold Joints
Identifying Poor Wetting
You can find poor wetting by looking at solder joints. Poor wetting means solder does not spread out well. The solder might look dull or bumpy. Sometimes, it forms a ball instead of a smooth line. X-ray inspection helps you see these problems. The table below shows what to look for:
Indicator Type | Descripción |
|---|---|
These show different joint shapes in x-ray pictures. You can tell if reflow happened. | |
Low magnification x-ray view | Lets you check many joints at once without moving the board. |
Comparison of joint shapes | Different shapes show if the reflow process worked or not. |
Causes of Cold Joints in Soldering
Cold solder joints happen when solder does not melt right. Here are some reasons why this happens:
Pads or leads are dirty.
There is not enough flux in the solder paste.
Soldering conditions are not controlled.
These problems make weak connections and more solder defects.
Solder Defects Impact
Poor wetting and cold joints can make your product less reliable. You might see:
Bad electrical flow, which can cause voltage drops and device problems.
Connections that work sometimes and fail other times.
Solder joints that crack or break from shaking or heat.
High resistance in the joint, which can make things overheat and break.
A wetting angle under 90° means a strong bond. If the angle is over 90°, the connection is weak and defects happen more. Solder bridging and tombstoning can also happen if wetting is bad.
Solutions for Wetting Issues
You can fix wetting problems and get fewer solder defects by doing these things:
Corrective Action | Descripción |
|---|---|
Change the temperature so gases leave before solder melts. | |
Solder Paste Selection | Pick paste with good flux and the right thickness. |
Stencil Design and Printing | Use a good stencil and put solder paste on evenly. |
Component and PCB Preparation | Clean all parts before you start soldering. |
Control Reflow Soldering Process | Set reflow settings for even heat and good wetting. |
Maintain Clean Work Environment | Keep your work area clean from dust and oil. |
Use High-Quality Materials | Use good solder paste for better results. |
Proper Handling and Storage | Store solder paste and parts in dry, safe places. |
Optimize PCB Design | Make sure solder mask covers the right spots to stop bridging. |
Regular Equipment Maintenance | Keep your reflow oven and printers working well. |
Training and Process Control | Teach your team to find and fix soldering problems. |
Quality Control and Inspection | Use AOI systems to check for defects after reflow. |
You can lower the chance of tombstoning and solder bridging by following these steps. Good process control and regular checks help you stop common soldering problems.
Voiding in Solder Joints
What Is Voiding?
Sometimes, you see empty spots inside solder joints. These spots are called voids. Voids happen when gases get stuck in the solder as it melts and cools down. Voiding is a common solder defect in electronics. If you do not control voids, you can get weak connections and more problems.
Voids look like bubbles or holes inside the solder. You can find them with x-ray or by checking for weak joints.
Causes of Voiding
Engineers found some main reasons for voiding in reflow soldering:
Solder paste lets out gases that get trapped in the solder.
Bad reflow settings keep gases inside and cause uneven melting.
Dirty PCB or parts stop solder from sticking well.
Pad size or thermal relief patterns can make more voids.
You should watch for these problems to lower solder defects and stop solder bridging.
Impact on Reliability
Voids in solder joints can make your product less reliable. You may see these problems:
Voids raise resistance and lower conductivity in solder joints.
Big voids or ones near the edge make joints weaker.
Voiding can cause heat stress and early failure.
If there are too many voids, the joint may break, especially in BGA packages.
Solder defects like voids can cause overheating and damage. You want to keep voids small and few to protect your products.
Solutions and Troubleshooting Guide
You can use different ways to lower voids and get better solder joints. Here is a troubleshooting guide to help you:
Paso | Descripción |
|---|---|
Optimize Reflow Profile | Change temperature, time, and air to help gases escape and lower voids. |
Use Appropriate Solder Paste | Choose low-voiding solder paste for better joints. |
Employ Vacuum Reflow | Use vacuum reflow to pull out trapped gases and lower voids. |
Slow ramp rate between 1°C and 3°C per second helps gases escape.
Soak phase at 155°C to 185°C for 30 to 120 seconds gives even heating.
Peak phase at 230°C to 245°C for lead-free soldering, holding for at least 45 seconds, makes joints stronger.
Tip: Clean all surfaces before soldering and check your reflow settings often. Good process control helps you stop solder defects like voids and solder bridging.
If you follow these steps, you can lower solder joint voiding and get stronger, more reliable solder joints.
Solder Balling Defects
What Is Solder Balling?
You might see small round solder balls on your PCB. These balls should not be there after reflow soldering. Solder balling happens when tiny solder pieces break away from the main joint. This can happen during the reflow process. You can find these defects near pads, between traces, or under parts. Solder balling is a common problem in soldering. If you do not fix it, it can cause many issues.
Causes of Solder Balling
Many things can make solder balling happen in reflow. You might use too much solder paste or put it on unevenly. If the stencil is dirty or the paste is too thick, solder balls can form. Fast heating can make the paste splatter. Moisture in the paste or on the PCB can also cause problems. Storing parts or paste the wrong way can make things worse. You need to watch for these issues to lower solder defects.
Soldering Defects and Risks
Solder balling can hurt your PCB in different ways. The table below shows the main risks:
Impact Type | Descripción |
|---|---|
Connectivity Issues | Solder balls can make unwanted electrical connections. This can lead to short circuits. |
Signal Integrity Compromise | Solder balls can mess up signals. This can cause voltage changes. |
Mechanical Stability Impairment | Solder balls can make the PCB less stable. This can make it break more easily. |
You want to stop these soldering problems. They can make your product fail or cause safety issues.
Solutions to Prevent Balling
You can use several ways to stop solder balling in reflow soldering:
Use the right amount of solder paste. Pick a good stencil design and check how the paste flows.
Make sure your PCB design is correct. Pad and solder mask designs should follow good rules.
Set the right temperature zones and ramp rates for your board and parts.
Store parts and paste the right way. Place components with care.
Keep the production area clean and control humidity. Take care of your equipment.
Tip: Check your process often and control it well. This helps you find solder balling early. If you follow these steps, you can lower solder defects and get better soldering results.
Insufficient and Excess Solder Paste
Insufficient Solder Paste Defects
If you use too little solder paste, problems can happen. Not enough solder means the joint may not form right. You might see weak connections or open circuits. Weak joints can break if you move the board. Sometimes, solder does not cover the pad all the way. The part may not stay in place. Dull or incomplete joints show there is not enough solder paste. This problem can make your product fail early.
Excess Solder Paste Issues
Using too much solder paste can cause bigger problems. Extra solder can flow between pads. This can make bridges that connect places that should not touch. Here are some common problems from too much solder paste:
Puente de soldadura between pads can cause short circuits.
Unwanted solder connections can lead to electrical failures.
Messy joints make inspection and repair harder.
Tip: Putting on the right amount of solder paste is important for good solder joints. Always check your paste amount before you start soldering.
You will see these problems more if you do not control the solder paste amount. Tight pad spacing can also make things worse. Bad profile control during soldering can add to the issue.
Solutions for Paste Application
You can stop these problems by using best practices for solder paste application. The table below shows some important steps:
Buenas prácticas | Descripción |
|---|---|
Choose the Right Solder Paste | Pick solder paste that fits your needs, including the right alloy and flux. |
Optimize PCB Design for Reflow | Make sure pad sizes and thermal mass match the soldering process. |
Create a Reflow Profile per Assembly | Set a custom thermal profile for each board to get the best solder joints. |
Control Cleanliness and Handling | Keep your work area clean to stop contamination during soldering. |
Use In-Line Inspection and Feedback | Check your work often and adjust your process to fix defects quickly. |
If you follow these steps, you will get better solder joints and fewer problems. Good control of solder paste helps you make strong and reliable products.
Reflow Soldering Profile Optimization
Importance of Temperature Profiles
You must set the right temperature for reflow soldering. A good temperature profile helps make strong solder joints. It also lowers the number of defects. When you control heat in each zone, you protect parts from damage. This stops problems like tombstoning and cold joints. It also helps prevent voids and solder balling. If you match solder type with the right heat, your products last longer. You get better results when you master preheat, soak, reflow, and cooling.
Strong control keeps solder joints reliable.
Each reflow zone has its own job.
Common Profile Mistakes
People often make mistakes when setting reflow profiles. These mistakes can cause soldering problems. They also lower the number of good boards. The table below shows common errors and what happens:
Defecto | Causa | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
Tombstoning | Uneven heating or solder paste | Part lifts, reliability drops |
Puente de soldadura | Pads too close together | Short circuits, board failure |
Insufficient wetting | Poor solder paste application | Weak joints, possible failure |
Solder balling | Fast ramp-up, too much paste | Solder balls, risk of shorts |
Check your process often to avoid these mistakes.
Troubleshooting Guide for Profile Settings
You can use a guide to fix profile problems in reflow soldering. Try these methods:
Method | Descripción |
|---|---|
Visual Inspection | Use a magnifier to find solder defects and solder balls. |
Electrical Testing | Use a multimeter to check for low resistance in solder joints. |
Thermal Cycling Tests | Heat and cool the board to test solder joint strength. |
Mechanical Stress Tests | Shake or tap the board to find loose or cracked joints. |
X-ray Imaging | Look inside joints for solder balls or voids. |
Tip: Always check your reflow oven and keep it working well. This helps you stop soldering problems early.
S&M Nitrogen Reflow Oven Solutions
You can fix many soldering problems with good equipment. S&M’s Nitrogen reflow oven gives advanced temperature control. The PID system keeps each zone steady within ±1°C. You get real-time monitoring to spot and fix issues fast. Cooling modules let you set cool rates over 3ºC per second. This meets tough lead-free reflow needs and helps stop solder balling. The flux system collects flux for easy cleaning. This means less downtime and better results.
S&M’s oven helps lower soldering defects and improve quality.
You get steady results with every reflow.
If you use these features and follow the guide, you can make strong solder joints and reduce solder balling in your assembly line.
PCB and Component Cleanliness
Cleanliness and Solder Defects
It is important to keep your pcb and parts clean before reflow soldering. Clean surfaces help make strong solder joints. Dirty boards or parts can cause many problems. Dirt or oil on the pcb can make weak joints. Bad connections can happen if things are not clean. Here are some ways cleanliness helps soldering:
A clean reflow oven keeps the temperature steady.
Things like flux residues can cause uneven heating.
Residues can stick to pcb assemblies and make solder not hold well.
If you do not keep things clean, you may get more soldering defects. You might see cold solder joints or even broken circuits.
Oils and chemicals can stop soldering from working right.
Dirty ovens can change temperature and cause cold joints.
Residues can stop solder from sticking and break circuits.
Common Contaminants
There are many types of contamination on pcb and parts before reflow. These can come from the board, the parts, or the machines you use. The table below shows some common contaminants and where they come from:
Contaminant | Source |
|---|---|
Copper | Comes from the circuit board surface finish |
Lead | Comes from tin-lead board surface finishes |
Iron | Comes from machine parts that touch solder alloys |
Gold | Comes from ENIG or hard gold processes |
Nickel | Comes from component leads with nickel coating |
These contaminants can make soldering harder and cause more defects.
Solutions for Clean Assembly
You can lower soldering defects by keeping everything clean. Here are some easy solutions:
Wash pcb and parts before reflow soldering.
Wear gloves to keep oil from your hands off the parts.
Clean the reflow oven often to remove old flux and dust.
Store boards and parts in dry, clean places.
Check for residues after each step in pcb assembly.
Tip: Make cleaning a regular part of your process. Clean tools and work areas help you get better solder joints and fewer problems.
If you follow these steps, you will have fewer soldering defects and stronger products.
Pad Design and Soldering Reliability
Pad Design Mistakes
Pad design can change how well soldering works. If you make pad layout mistakes, you can get many solder problems. Some common mistakes are pads that are not the same size, pads too close together, and pads that are too small. These issues can cause tombstoning, solder bridging, and weak joints. You should check your pcb layout before reflow to stop these problems.
He aquí un cuadro que muestra pad design mistakes, why they happen, and how to fix them:
Mistake | Root Cause | Suggested Fix |
|---|---|---|
Tombstoning | Uneven thermal mass; one pad connected to a large ground plane, the other isolated. | Use thermal reliefs to connect the pad to the ground plane for even heating. |
Pads too wide or insufficient solder mask dam between pads. | Follow IPC-7351 pad width calculations and ensure proper solder mask dam width. | |
Insufficient Solder | Pads too small leading to inadequate solder paste volume. | Use IPC-7351 Level B or A for robust designs, ensuring sufficient pad size and land extensions. |
Impact on Solder Defects
Bad pad design makes more solder problems in pcb assembly. Pads that are too close can make solder bridge between them. Pads with different thermal mass can cause tombstoning during reflow. Small pads may not hold enough solder, so joints are weak. You might see open circuits, short circuits, or joints that break. Poor pad design can also make contamination worse because solder may not flow or wet the pad right.
Tip: Always check your pad design before reflow soldering. Good design helps you stop many defects and keeps your pcb strong.
Solutions for Reliable Soldering
You can use different ways to make soldering better. First, follow IPC-7351 rules for pad size and spacing. Use thermal reliefs for pads on big copper areas. Make sure the solder mask dam is wide enough to stop bridging. Pick the right pad size to hold enough solder paste. Clean your pcb and pads before reflow to lower contamination. If you do these things, you will get fewer solder problems and stronger joints.
Check pad layout for each pcb before making it.
Use the right pad sizes and solder mask widths.
Clean all surfaces to stop contamination.
Watch reflow profiles to keep heating even.
You can get better soldering and fewer problems by focusing on pad design and process control.
You can have fewer defects in reflow soldering if you find mistakes early and fix them. S&M’s Nitrogen reflow oven and reflow oven help keep soldering even and steady. If you use the troubleshooting guide, you can make your work better and get good results. Try to use these steps every day. Your solder joints will be stronger and you will have less trouble on your assembly line.
PREGUNTAS FRECUENTES
What is the most common mistake in reflow soldering?
You often see too much or too little solder paste. This mistake causes weak joints or solder bridges. Always check your paste amount before you start.
How can you quickly spot solder defects?
Use a magnifier or AOI system to check joints after reflow. Look for dull, cracked, or uneven solder. These signs show defects.
Why does temperature control matter in reflow soldering?
Temperature control helps you make strong solder joints. If the oven gets too hot or too cold, you get more defects like tombstoning or cold joints.
What equipment helps reduce soldering defects?
Tipo de equipo | Beneficio |
|---|---|
Precise temperature control | |
AOI System | Fast defect detection |
S&M’s Nitrogen reflow oven gives you steady heat and fewer defects.
How do you keep PCBs clean before soldering?
You should wash boards and parts. Wear gloves to stop oil from your hands. Store everything in a dry, clean place.
