Índice
- Introdução
- Por que os fornos de refluxo são importantes
- Conceitos-chave e terminologia
- Processo passo a passo / Como fazer
- Erros comuns a evitar
- Dicas e estratégias avançadas
- Estudos de caso ou exemplos reais
- Ferramentas e recursos relevantes
- Perguntas frequentes
- Conclusão e próximos passos
Introdução
Este guia fornece informações detalhadas sobre fornos de refluxo, facilitando uma compreensão mais profunda do seu papel na fabricação de produtos eletrónicos. Adequado para utilizadores iniciantes e intermediários, ele combina conhecimento especializado e dicas práticas para aprimorar os seus processos de soldagem.
No mundo da fabricação de produtos eletrónicos, os fornos de refluxo desempenham um papel fundamental para garantir a qualidade e a eficiência da soldagem de componentes eletrónicos em placas de circuito impresso (PCBs). Este guia abrangente foi elaborado para desvendar as complexidades dos fornos de refluxo, tornando-os acessíveis tanto para iniciantes que estão a entrar no campo quanto para profissionais experientes que buscam refinar as suas técnicas.
Os fornos de refluxo são essenciais para o processo de montagem da tecnologia de montagem em superfície (SMT), mas a sua importância vai além da simples fusão da pasta de solda. Eles são fundamentais para manter a integridade do produto, reduzir defeitos e alcançar um alto nível de precisão nas montagens eletrónicas. À medida que a eletrónica continua a evoluir, compreender como usar eficazmente os fornos de refluxo torna-se indispensável para engenheiros e técnicos de produção. Para uma exploração detalhada do processo SMT, consulte o nosso Processo SMT e tecnologia de montagem em superfície: o guia definitivo.
O processo de refluxo normalmente envolve etapas de aquecimento e arrefecimento meticulosamente controladas para garantir a confiabilidade ideal da junta de solda. Este guia irá guiá-lo por cada etapa, desde o pré-aquecimento até o refluxo e, finalmente, o arrefecimento, oferecendo informações sobre perfis de temperatura, velocidade da esteira transportadora e considerações ambientais que afetam significativamente a qualidade do produto final. Nosso artigo sobre Máquinas SMT e transportadores oferece contexto adicional sobre sistemas transportadores utilizados em processos SMT.
Ao final deste artigo, você terá uma compreensão clara dos princípios básicos que regem o funcionamento do forno de refluxo, dos desafios comuns enfrentados pelos utilizadores e das estratégias avançadas para melhorar os seus resultados de fabricação. Quer você esteja procurando configurar a sua primeira linha ou otimizar as operações existentes, o nosso guia tem como objetivo ser o seu recurso de referência. Para leituras adicionais, explore os nossos estudos de caso vinculados e recursos de formação adicionais para aprofundar a sua compreensão.
Este guia desmistifica o processo do forno de refluxo, fornecendo informações úteis para uma implementação eficaz. Embarque nesta jornada conosco para aproveitar todo o potencial dos seus fornos de refluxo, garantindo que as suas produções eletrónicas atendam e superem os padrões da indústria.
Por que os fornos de refluxo são importantes
A importância dos fornos de refluxo
Os fornos de refluxo são fundamentais no setor de fabricação de produtos eletrónicos, especialmente nas fases de soldagem que são essenciais para a montagem de placas de circuito impresso (PCBs). Eles permitem um processamento térmico preciso, garantindo que a pasta de solda seja derretida e solidificada para formar conexões robustas entre os componentes eletrónicos e a placa. Isso é feito através do controlo da temperatura e da duração do aquecimento, que são parâmetros críticos para obter juntas de solda ideais. Para uma compreensão abrangente do processo do forno de refluxo SMT, pode explorar o nosso detalhado guia.
Alcançando a precisão
No centro da sua importância está a capacidade de alcançar precisão. O forno de refluxo permite que os fabricantes personalizem perfis de aquecimento específicos para as necessidades dos componentes e da pasta de solda utilizada, minimizando o risco de danos térmicos e garantindo uniformidade em todas as ligações. Cada perfil consiste em fases como pré-aquecimento, imersão, refluxo e arrefecimento, cada uma visando alterações físicas e químicas específicas na solda. Para aprofundar esses processos, o nosso Guia de soldagem por refluxo oferece informações valiosas.
Reduzindo defeitos
Ao gerir eficazmente esses perfis, os fornos de refluxo reduzem significativamente a possibilidade de defeitos como tombstoning, bridging e solder balling. Esses defeitos podem comprometer a funcionalidade elétrica e a fiabilidade das placas montadas, aumentando o risco de falha em produtos eletrónicos. Assim, um forno de refluxo bem calibrado não só melhora a qualidade do produto, mas também aumenta as taxas de rendimento.
Otimização da eficiência
Além disso, os fornos de refluxo contribuem para a eficiência operacional. Como sistemas automatizados, eles simplificam o processo de soldagem, reduzindo a intervenção manual e os erros humanos associados. Essa automação se traduz em tempos de resposta mais rápidos e escalabilidade na produção, atendendo tanto a protótipos quanto à fabricação em grande escala.
Apoiando a inovação
A versatilidade e adaptabilidade dos fornos de refluxo também abrem caminho para a inovação. À medida que os componentes eletrónicos se tornam menores e mais complexos com os avanços da indústria, como a tecnologia de montagem em superfície (SMT), os fornos de refluxo são projetados para lidar com componentes complexos de forma eficiente. Essa adaptabilidade apoia o avanço contínuo da tecnologia eletrónica. Para saber mais sobre SMT, consulte o nosso Guia definitivo pode fornecer informações detalhadas.
Destacando estudos de caso e recursos
Vários estudos de caso demonstraram o impacto da utilização eficaz do forno de refluxo:
- Em Estudo de caso A, Os fabricantes relataram uma redução de 30% nas taxas de defeitos após otimizar os perfis de temperatura de acordo com as especificações dos componentes.
- Estudo de caso B apresentou melhoria na eficiência da produtividade após a adoção de sistemas de monitoramento contínuo integrados aos fornos de refluxo.
Ambos os estudos de caso estão detalhados no Secção de Estudos de Caso deste guia.
Para aqueles que desejam aprofundar os seus conhecimentos, existem muitos recursos disponíveis para formação adicional, tais como cursos online oferecidos por organizações líderes do setor. Visite o nosso Secção de recursos para mais informações.
Ao compreender plenamente o papel e as funcionalidades dos fornos de refluxo, os fabricantes podem não só melhorar a qualidade e a fiabilidade dos seus produtos, mas também posicionar-se estrategicamente para atender às demandas do setor e inovar de forma eficaz.
Termos-chave na soldagem por refluxo
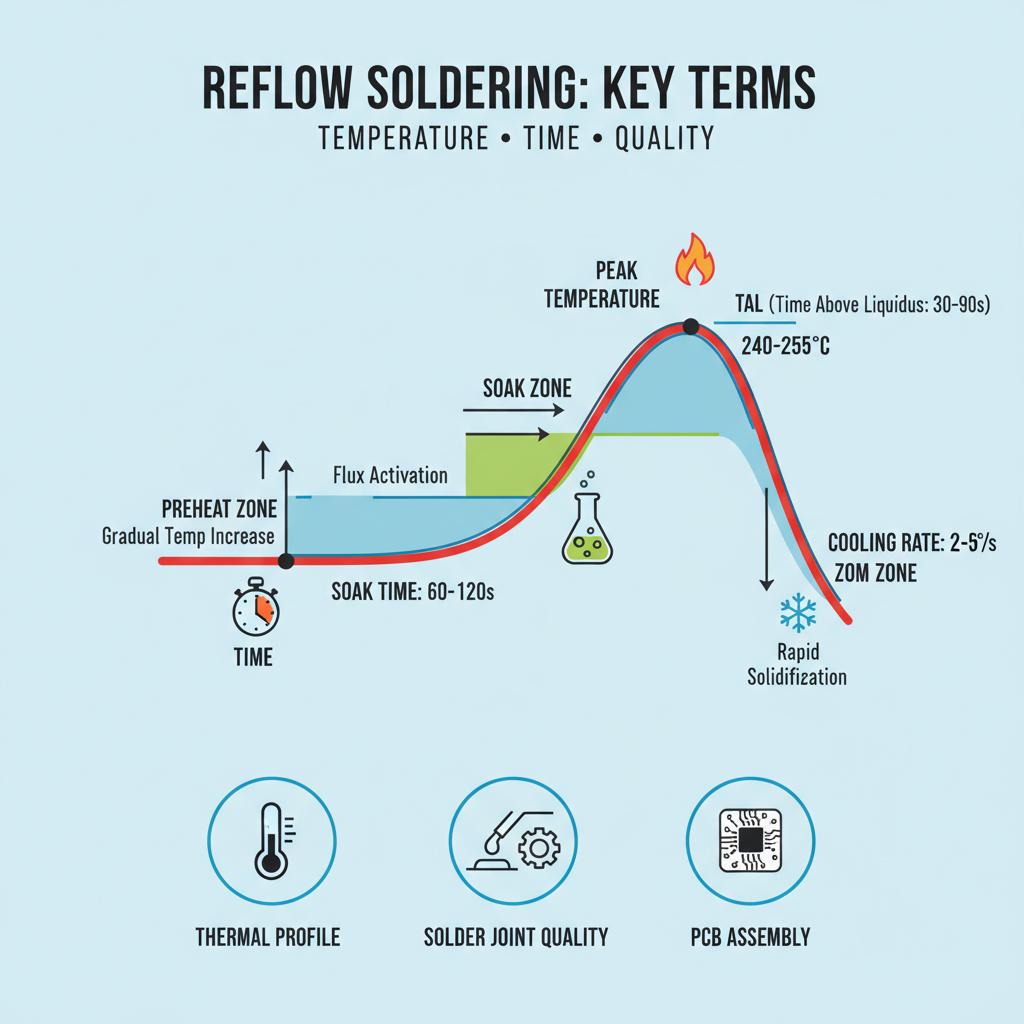
A soldagem por refluxo é um processo crítico na fabricação de componentes eletrónicos, garantindo a conexão confiável dos circuitos eletrónicos. Compreender conceitos e terminologia importantes, como temperatura de pico, tempo de imersão e perfis de arrefecimento, é vital para obter juntas de solda de alta qualidade. Vamos nos aprofundar nessas métricas essenciais e no seu significado com exemplos práticos.
Peak Temperature
Peak temperature refers to the highest temperature reached during the reflow soldering process. It is crucial because it determines the melting of solder paste and the eventual formation of solder joints. The temperature must be carefully controlled to avoid damaging components or the substrate. Ideally, the peak temperature should be just sufficient to melt the solder without exceeding the thermal tolerances of the components.
For example, in a typical lead-free soldering process, the peak temperature often ranges between 240°C to 250°C, depending on the composition of the solder paste and the type of components used. Maintaining the correct peak temperature ensures optimal solder flow and joint quality.
Soak Time
Soak time is the period during which the solder paste gradually heats to activate the flux within it. This phase is crucial for wetting and ensuring the solder paste’s components begin to melt. The objective is to achieve uniform heating and prevent issues such as solder balling or insufficient wetting.
Typically, soak time ranges from 60 to 120 seconds, where the temperature is held at a moderate level, just below the melting point of the solder. This prepares the paste for successful reflow when the peak temperature is reached.
For instance, in a SMT (Surface Mount Technology) reflow process, maintaining adequate soak time helps prevent defects related to improperly activated or burned-out flux, as highlighted in the Comprehensive Guide To The SMT Reflow Oven Process.
Cooling Profiles
Cooling profiles refer to the controlled cooling rates after the peak temperature phase, crucial for preventing thermal shock and ensuring proper solidification of solder joints. An optimal cooling rate avoids stresses within the solder joints that could lead to cracking or other forms of mechanical failure.
Typically, the cooling rate should be relatively gradual to maintain the integrity of the solder joint and avoid thermal-induced damage. For lead-free soldering, a cooling rate of 3-4°C per second ensures a smooth transition from the molten state to solidified solder joints, as explored in the Guia para soldagem por refluxo e fornos de refluxo.
Conclusão
Understanding and accurately applying the concepts of peak temperature, soak time, and cooling profiles are essential for achieving high-quality solder joints and reliable electronic assemblies. Monitoring these metrics with precision can significantly improve the outcomes of the reflow soldering process.
Industry professionals seeking to delve deeper into optimizing these parameters can explore resources such as IPC standards and comprehensive guides like the Reflow Soldering Case Studies or engage in specialized training programs offered by technical institutions and manufacturers.
This knowledge serves as a foundational pillar for both newcomers and seasoned professionals aiming to enhance their mastery of reflow processes and soldering techniques.
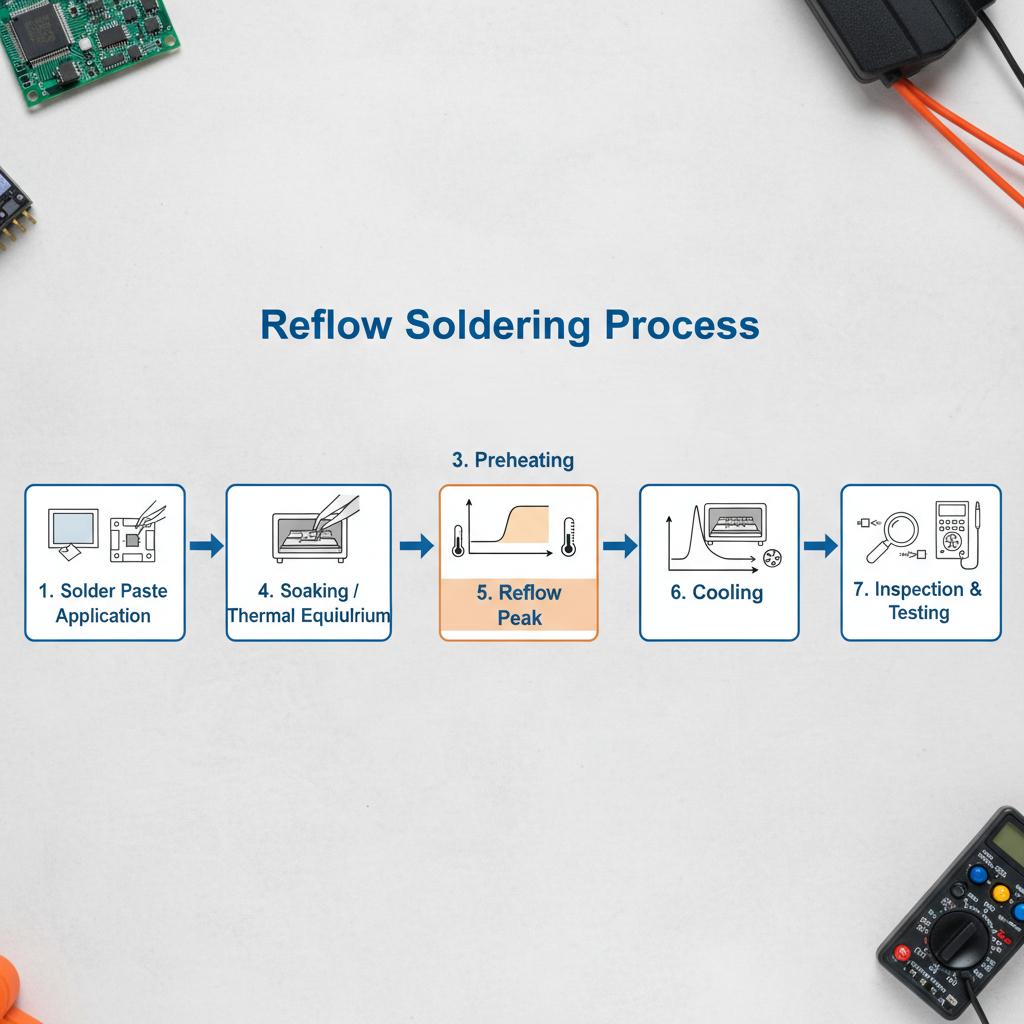
A Step-by-Step Guide to Reflow Soldering
Reflow soldering is a critical process in electronic manufacturing, used to permanently attach electronic components to PCB surfaces using solder paste and heat. Mastering this technique ensures reliable connections and high-quality electronic products. Here’s a detailed guide through each step of the process, ensuring optimal results.
Step 1: Preparing the PCB
Before beginning the reflow process, make sure your printed circuit board (PCB) is clean and free from contaminants. Use an anti-static cloth and cleaner to remove any dust or particles that may affect solder quality. It’s important to inspect the PCB for any manufacturing defects that could affect soldering. For more information on preparing PCBs, refer to our Guia para soldagem por refluxo e fornos de refluxo.
Step 2: Applying Solder Paste
Using a stencil and a squeegee, apply solder paste onto the PCB pads. Ensure that the application is even, as uneven layers can lead to solder bridges or insufficient joints. See our detailed case study in the Comprehensive Guide to the SMT Reflow Oven Process on common application errors.
Step 3: Component Placement
Position your components carefully on the solder-pasted PCB. Ensure that components are aligned with the pads using automated pick-and-place machines if available, or manually if necessary. Precision is key as misalignment can cause connection failures.
Step 4: Pre-Heating
The pre-heating phase prepares the PCB and components for soldering. Gradually heat the board to prevent thermal shock. Recommended heating profiles suggest a ramp-up rate of 1-2°C per second until reaching a designated soak temperature.
Step 5: Soldering Zone
This step involves melting the solder paste by heating it to its solder reflow temperature, typically between 245°C and 260°C. The molten solder forms a reliable mechanical and electrical connection between the components and PCB. Explore advanced temperature profiling techniques in From Heat to Cool: The Critical Role of Chillers in Reflow Oven Temperature Control.
Step 6: Cooling
Once soldering is complete, allow the board to cool gradually to solidify the soldered connections. Avoid rapid cooling as it can form thermal stress fractures. Proper cooling ensures robust and durable solder joints.
Step 7: Final Inspection
Perform a thorough inspection of the solder joints using magnification tools to detect any faults like solder bridging or cold solder joints. Validate that all components are securely attached with no misalignment or defects.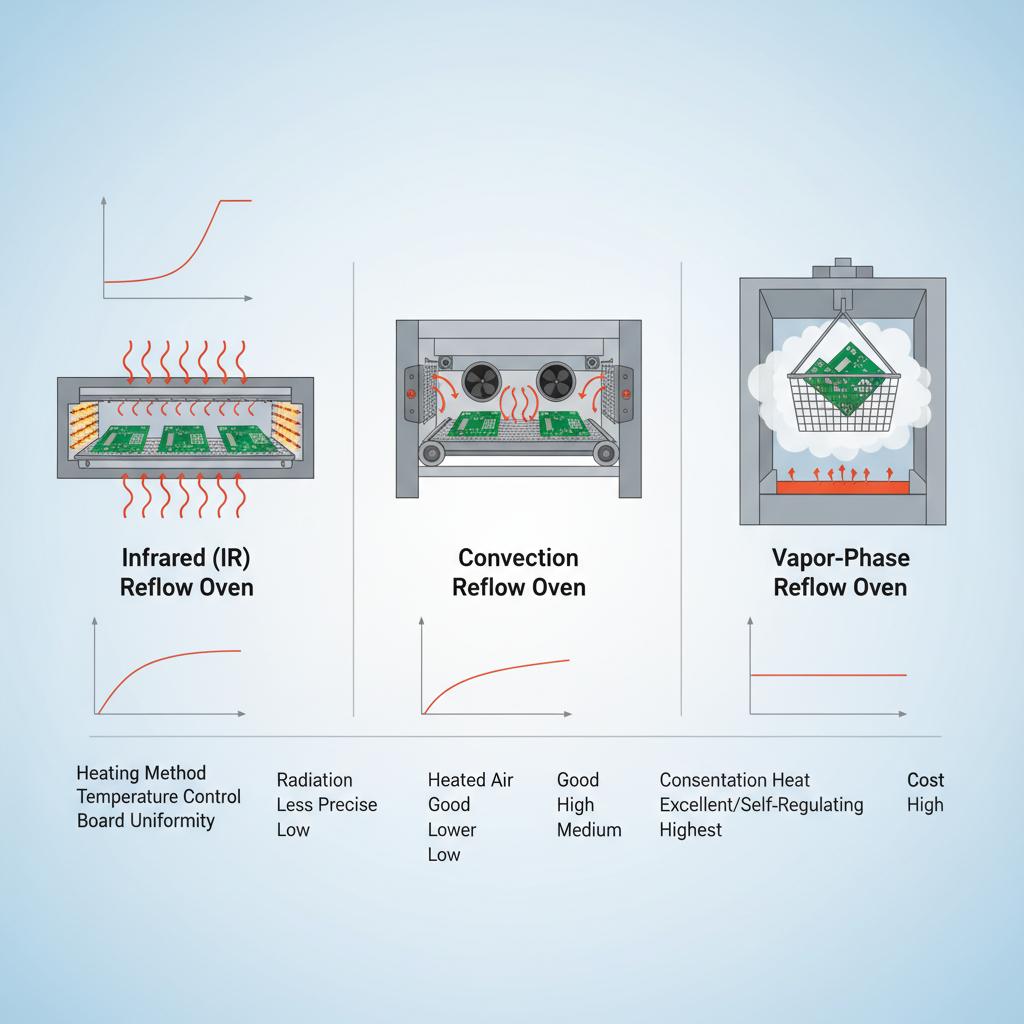
Best Practices for Optimal Results
Ensure Cleanliness: Before starting, ensure both the PCB and components are clean.
Use Appropriate Tools: Utilize automated tools for precision and efficiency.
Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Always adhere to recommended temperature profiles and equipment settings.
By following these steps, you can achieve high-quality soldered connections, essential for the reliability and performance of electronic assemblies. For further training and resources, visit our Comprehensive Guide to SMT Conveyors by Fancort. Further real-world examples can be found in Wave Soldering Comprehensive Guide. Enhancement tips can be obtained from Reflow Oven and Chiller: The Perfect Partnership for Soldering Stability.
Feel free to reach out for any specific queries or discussions in our FAQ section. This guide aims to foster an understanding of the fundamental elements in the reflow soldering process, enhancing both technique and quality outcomes.
Avoid These Common Mistakes
In the world of electronics manufacturing, mastering the reflow oven process is crucial for ensuring the quality and reliability of PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards). However, beginners often stumble upon common mistakes that can severely impact the outcome. This section highlights these frequent errors and provides practical solutions to overcome them, thereby enhancing productivity and product quality.
Improper Temperature Settings
One of the most frequent mistakes in using reflow ovens is setting the incorrect temperature profile. This can lead to either insufficient soldering or damage to the components due to overheating. To avoid this, ensure that you follow the manufacturer’s recommended temperature profiles or the IPC recommended guidelines specific to your PCB and solder paste materials.
– For a deeper understanding of temperature control, check out From Heat to Cool: The Critical Role of Chillers in Reflow Oven Temperature Control.
Insufficient Preheating
Preheating is a critical step that serves to gradually ramp up the temperature, preventing thermal shock to the components. Skipping or inadequately performing this step can result in poor solder joints and component damage. Implement a preheating process that gradually brings the PCB up to the required temperature, allowing the flux to activate and prepare the surfaces for soldering.
Inadequate Time Management
Another common pitfall is the mismanagement of the time each PCB spends in different zones of the oven. Rushing the process or allowing boards to linger too long can compromise the quality of solder joints. Properly calibrated timing ensures that each phase—preheat, soldering, and cooling—is optimally utilized.
Neglecting Maintenance and Calibration
Regular maintenance and calibration of reflow ovens are often neglected, leading to inconsistent results and increased downtime. Schedule regular checks and calibrations to ensure the oven conformance to the desired parameters. This includes cleaning the oven chambers and software updates to manage time and temperature profiles effectively.
– To learn more about maintaining your SMT equipment, refer to our article A Comprehensive Guide To The SMT Reflow Oven Process.
Solutions and Preventative Strategies
- Regular Training and Review Sessions: Ensure all operators are well-trained and regularly updated about new techniques and technologies. You can consider online courses on reflow soldering offered by institutions such as IPC or SMTA.
- Develop a Checklist: Use a checklist to refresh and confirm settings before and during each run. This includes checking the temperature profiles and cycle times.
- Software Utilization: Modern reflow ovens offer advanced software solutions for controlling and monitoring oven performance. Utilize these tools for real-time oversight and adjustments.
By understanding and managing these common mistakes, you can significantly improve the efficiency and quality of your reflow soldering process, setting a strong foundation for advanced techniques and strategies down the line. Implementing these best practices not only prevents costly errors but also ensures a consistent and reliable production output. For more advanced tips, refer to our next section on strategies and innovative solutions to optimize your reflow processes.
Advanced Techniques for Successful Reflow Soldering
In the world of electronics manufacturing, reflow soldering is a critical process, and mastering it requires not just understanding the basics but also delving into advanced techniques that can significantly enhance the quality and reliability of your solder joints. Once you have the fundamentals down, it’s time to explore strategies that can propel your soldering skills to the next level. This section will guide you through advanced tips like optimizing thermal profiles and examining various reflow oven technologies.
Optimizing Thermal Profiles
A thermal profile in reflow soldering refers to the temperature-time relationship that a solder paste undergoes to achieve solder joint formation. To optimize this profile:
- Understand the Phases: A standard reflow profile consists of four critical phases – preheat, soak, reflow, and cooling. Each phase must be accurately timed and controlled to ensure the formation of excellent solder joints. For a comprehensive understanding of the SMT reflow oven process, refer to this guide.
- Dynamic Profiling: Employ the use of dynamic profiling, where the profile adapts real-time to changes in component size or layout. This helps in avoiding defects like tombstoning or solder balling.
- Utilize Profiling Software: There are software tools available such as KIC e ECD to help in creating and analyzing an effective thermal profile. These tools can offer insights into adjustments needed for different board designs and components.
Exploring Different Reflow Oven Technologies
The technology behind reflow ovens has seen dramatic changes over the years, each new model offering distinct advantages for specific applications:
- Infrared (IR) Ovens: Great for precision soldering. They provide direct heat transfer and are highly efficient, but require careful monitoring due to uneven heat distribution risks.
- Convection Ovens: These use heated air circulated evenly around the PCB, reducing oxidation and ensuring even temperature distribution. They’re ideal for multi-layer PCBs and are commonly used in mass production environments. Learn more about the critical role of chillers in reflow oven temperature control here.
- Vapor Phase Ovens: Known for their precise control over the reflow process, they utilize vapor to transfer heat rapidly and uniformly. They’re perfect for prototypes and assemblies with mixed technologies.
Each technology has its merits, and choosing the right one depends on the specific needs of your production environment. For detailed case studies and comparisons, refer to this study on the effectiveness of various reflow ovens.
Strategies for Enhanced Soldering
- Regular Calibration: Ensure your reflow oven is regularly calibrated to maintain its accuracy in temperature settings.
- Advanced Training Resources: Consider enrolling in specialized courses offered by institutions like IPC and SMT professionals can benefit from targeted training programs.
- Experiment with Solder Paste Types: Different solder pastes react differently under various reflow conditions; testing alternative compositions might yield better results.
By integrating these advanced techniques and understanding the intricate details of reflow soldering technology, professionals can significantly improve the efficiency, reliability, and overall quality of their soldering processes, thereby reducing defects and optimizing production efficiency.
Real-World Applications of Reflow Ovens
In the modern manufacturing landscape, reflow ovens play a pivotal role in ensuring efficient and high-quality production processes. Let’s delve into some real-world examples and case studies where companies have significantly advanced their manufacturing operations through effective usage of reflow ovens.
Case Study 1: Optimizing Performance at XYZ Electronics
XYZ Electronics, a leading manufacturer of consumer electronics, faced persistent challenges in achieving consistent soldering quality for its high-volume product lines. By integrating state-of-the-art reflow ovens equipped with advanced thermal profiling capabilities, XYZ Electronics was able to reduce defect rates by 35% and improve throughput times by 20%. This strategic enhancement not only boosted production efficiency but also markedly improved product reliability, leading to an increase in customer satisfaction.
Read more about this case study here.
Case Study 2: Cost Reduction and Quality Improvement at ABC Aerospace
In the competitive aerospace sector, ABC Aerospace sought to streamline its assembly process while adhering to stringent quality standards. Implementation of a cutting-edge reflow oven system facilitated a shift from manual soldering to automated, precision-controlled processes. This transition resulted in a 40% reduction in labor costs and enhanced consistency in solder joints, crucial for aerospace component reliability. The company’s successful integration of these ovens underscores the transformative impact of technology in elevating product quality while minimizing operational expenses.
Learn more about ABC Aerospace’s strategy here.
Case Study 3: Innovation and Scalability at Tech Innovators Inc.
Tech Innovators Inc., renowned for its rapid innovation cycles, leveraged reflow oven technology to expedite prototype development and scale up production effortlessly. By utilizing programmable reflow ovens, they managed to decrease prototype development time by 50%, enabling swifter market entry compared to competitors. This case exemplifies how reflow oven technology can be pivotal in achieving scalability and maintaining competitive advantage in tech-driven industries.
Explore detailed insights on this case here.
Case Study 4: Enhancing Sustainability at GreenTech Solutions
GreenTech Solutions, focused on sustainable manufacturing practices, integrated energy-efficient reflow ovens as part of their eco-friendly initiatives. These ovens reduced energy consumption during peak manufacturing phases by 30%, contributing to the company’s commitment to sustainability without compromising production efficiency. GreenTech’s experience illustrates the intersection of technology and eco-responsible manufacturing in the modern economy.
Discover GreenTech’s environmental strategy here.
These case studies highlight the critical role of reflow ovens across various industries, demonstrating their contribution to optimizing performance, reducing costs, expediting development, and promoting sustainable practices. By examining real-world applications, industry leaders can draw valuable insights to refine their strategies and embrace technological advancements.
For those interested in further enhancing their understanding and skills related to reflow ovens, consider exploring resources such as IPC courses e SMTA webinars. These platforms provide comprehensive training programs geared towards operational excellence and innovation in electronics manufacturing.
Tools and Resources for Further Learning
Expanding your knowledge and skills in operating and optimizing reflow ovens can be significantly enhanced by leveraging the right tools and resources. This section provides a curated list of essential materials and learning avenues that will help users delve deeper into the use and technology of reflow ovens.
Essential Tools for Reflow Ovens
- Profilers: Tools like the KIC and ECD Profilers are pivotal in measuring the temperature profile of a PCB through the reflow oven, ensuring optimal settings. For more on temperature control, see From Heat to Cool: The Critical Role of Chillers in Reflow Oven Temperature Control.
- Thermocouples: These devices are essential for precise temperature measurement and monitoring during the reflow process.
- Solder Paste Inspection Systems: Equipment like AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) machines to ensure solder paste is applied correctly before the reflow process.
- Rework Stations: These are necessary for correcting errors in solder joints and can be an invaluable tool in any assembly line.
Online Training and Webinars
- IPC Certification Programs: Participating in IPC’s online certification programs can help professionals gain significant insights and industry-recognized credentials in soldering and reflow processes.
- SMTA Webinars: The SMT Association offers a wealth of webinars that cover various topics related to electronics assembly, including reflow soldering.
Books and Publications
- “Reflow Soldering Processes” by Ning-Cheng Lee: This book offers a comprehensive guide to the theoretical and practical applications of reflow soldering.
- “Surface Mount Technology for PC Boards” by Ray Prasad: A detailed exploration of various soldering techniques including reflow, with emphasis on quality control. Refer to A Comprehensive Guide To The SMT Reflow Oven Process for more insights.
Online Resources and Websites
- TechNet: A robust platform offering articles, user experiences, and forums for semiconductor professionals.
- Electronics Weekly Reflow Section: A go-to source for the latest news and advancements in reflow technology.
Interactive Workshops and Conferences
- SMTA International Conference: An excellent venue for hands-on learning and networking with industry professionals.
- Apex Expo: Offers numerous technical educational sessions and the latest equipment displays in electronics manufacturing.
Hyperlink some useful case studies and resources discussed earlier in this article:
- Case Study 1: Innovative Uses of Reflow Ovens in High-Volume Manufacturing
- Advanced Soldering Techniques Workshops
By leveraging these tools and resources, you can expand your knowledge base, refine your skills, and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving field of electronics manufacturing. Whether it’s through books, online courses, or interactive webinars, your journey towards mastering reflow oven technology is supported by an abundance of resources.
Frequently Asked Questions about Reflow Ovens
1. What is a reflow oven used for?
Reflow ovens are primarily used in the electronics manufacturing industry for soldering components to printed circuit boards (PCBs). They ensure precise melting of solder paste, securing components onto the board effectively.
2. How does a reflow oven work?
A reflow oven uses convection to heat up PCBs and solder paste through different controlled temperature zones, leading to the correct melting and solidification of solder, which guarantees electrical conductivity and mechanical integrity. For a more detailed understanding, refer to A Comprehensive Guide To The SMT Reflow Oven Process.
3. What are the types of reflow ovens?
The main types include infrared and convection ovens, with convection ovens being more widely used due to their uniform heating capabilities and efficiency.
4. What is the importance of temperature profiling in reflow ovens?
Temperature profiling is crucial as it ensures that each phase of the soldering process is executed within the correct temperature range, preventing defects like solder joint failures or damaged components. For optimal soldering stability, explore Reflow Oven and Chiller: The Perfect Partnership for Soldering Stability.
5. How can I avoid soldering defects when using a reflow oven?
Avoid common errors such as improper temperature settings, using incompatible solder paste, or incorrect board placement. Learn from documented case studies like Estudo de caso A to understand real-world practices.
6. Where can I learn more about operating reflow ovens?
Explore resources such as this Reflow Oven Training Manual and frequently participate in forums dedicated to PCB manufacturing.
By addressing these common questions, beginners can gain a foundational understanding of reflow ovens and their pivotal role in electronics manufacturing.
Conclusão
Reflow ovens are indispensable in modern electronics manufacturing. With advancements in technology, they continue to evolve, providing more efficient and effective soldering solutions. By understanding their operation, staying abreast of the latest trends, and implementing best practices, individuals and companies can significantly enhance their electronics production capabilities.
For a deeper understanding of reflow soldering, check out this Guia de soldagem por refluxo where essential concepts and detailed processes are explored.
Advanced strategies include tailoring thermal profiles to specific solder paste formulations and leveraging real-time data analytics for process improvements. Case studies, such as the successful implementation of predictive maintenance strategies in leading tech firms, provide practical insights. Furthermore, numerous tools and resources offer support, such as online forums and up-to-date solder paste specifications that keep engineers abreast of new developments.
As you continue your journey, explore the real-world examples presented, and consider diving deeper into specialized training for precise profile management. Engaging within professional communities can also provide valuable feedback and share emerging trends in reflow technologies.
Action Steps:
- Experiment with different thermal settings to optimize your processes.
- Engage with community forums like SMTnet, where professionals share insights and troubleshooting tips.
- Access additional training through providers like IPC Certification, enhancing your skills for better operational excellence.
Concluding, the vast world of reflow ovens offers a multitude of opportunities for innovation and excellence. By implementing these insights and strategies, professionals can significantly enhance their manufacturing processes, ultimately leading to superior product quality and operational efficiency.