Introduction to Soldering Wave Technology
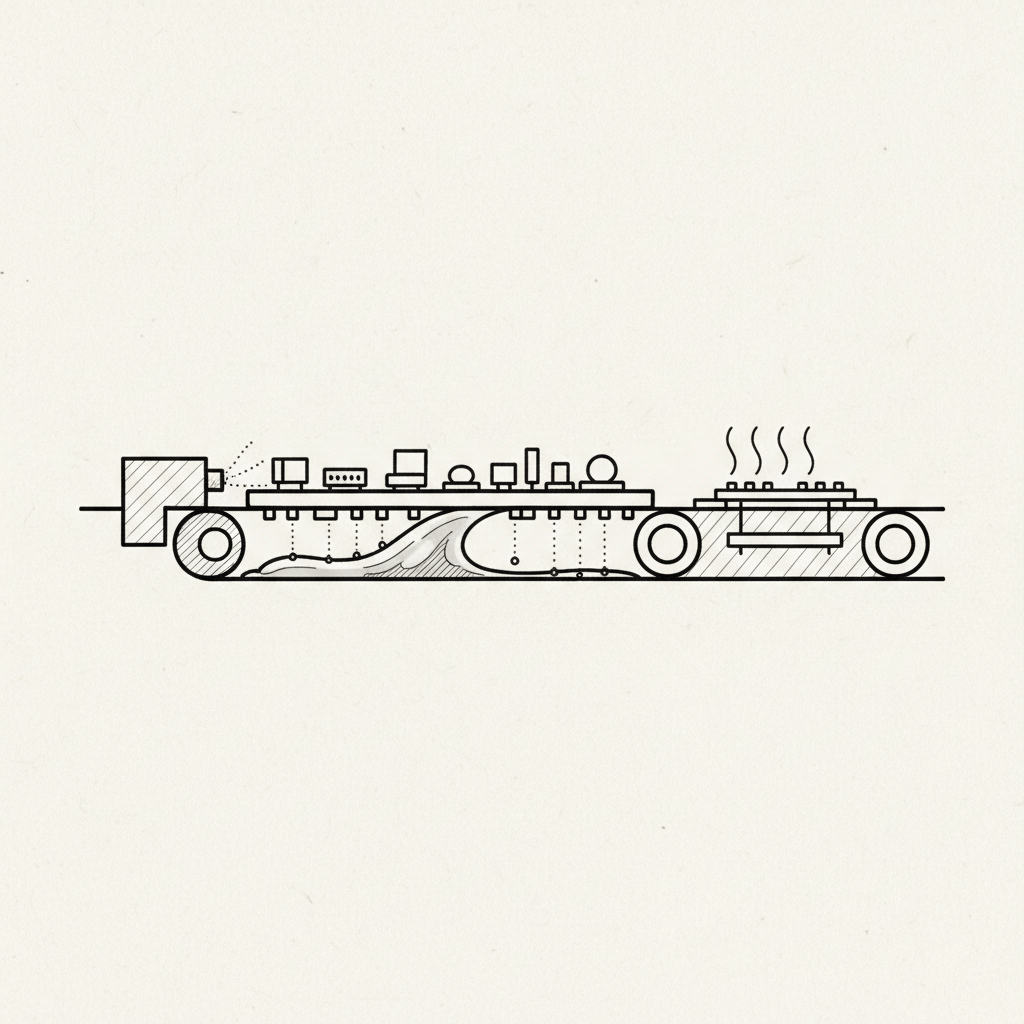
Soldering wave technology is a pivotal process in electronics manufacturing that involves the mass soldering of printed circuit boards (PCBs) featuring pre-inserted through-hole components.
Soldering wave technology is a pivotal process in electronics manufacturing that involves the mass soldering of printed circuit boards (PCBs) featuring pre-inserted through-hole components.
Wave soldering is a bulk soldering process utilized in electronics manufacturing that attaches through-hole components to printed circuit boards (PCBs) by passing the board over a wave of molten solder.